Nowadays, computers are used almost everywhere in our lives. A lot of people do different tasks on them as part of their work, they help us find information and entertain us, they are a great study tool. For instance, even now you are using a computer or a smartphone to read this article.
Given their wide presence, it can be helpful to learn to use computers more efficiently and even adapt them for our needs. The best way to do that is to learn to code.
As you may guess, the machine can't understand English or any other natural language we communicate in, so we need a different means of telling it what our objectives are. That is actually the function of programming languages.
A programming language is basically a special set of commands and functions that can be run directly by the machine. What we need to code is to learn the syntax of the programming language to structure our code in the right way.
There are dozens of programming languages that exist these days. They have all their strong and weak points, serve slightly different purposes and are more or less difficult to learn.
Why Python?
Probably, one of the easiest and most powerful programming languages for beginners is Python. Its huge advantage is that once you learn its basic functions, you can get access to numerous code libraries and customise Python for your particular goals.
Check out python class here.

That feature makes Python very flexible and it can actually be used in really diverse areas, such as data science, video-game development, creation of online apps or natural language processing, for example.
In this article, we will give you a short introduction to Python programming. If you understand a few essential concepts, you can begin to code very quickly and work with huge amounts of data effectively.
You can find more information about Python in our article.

Installing Python
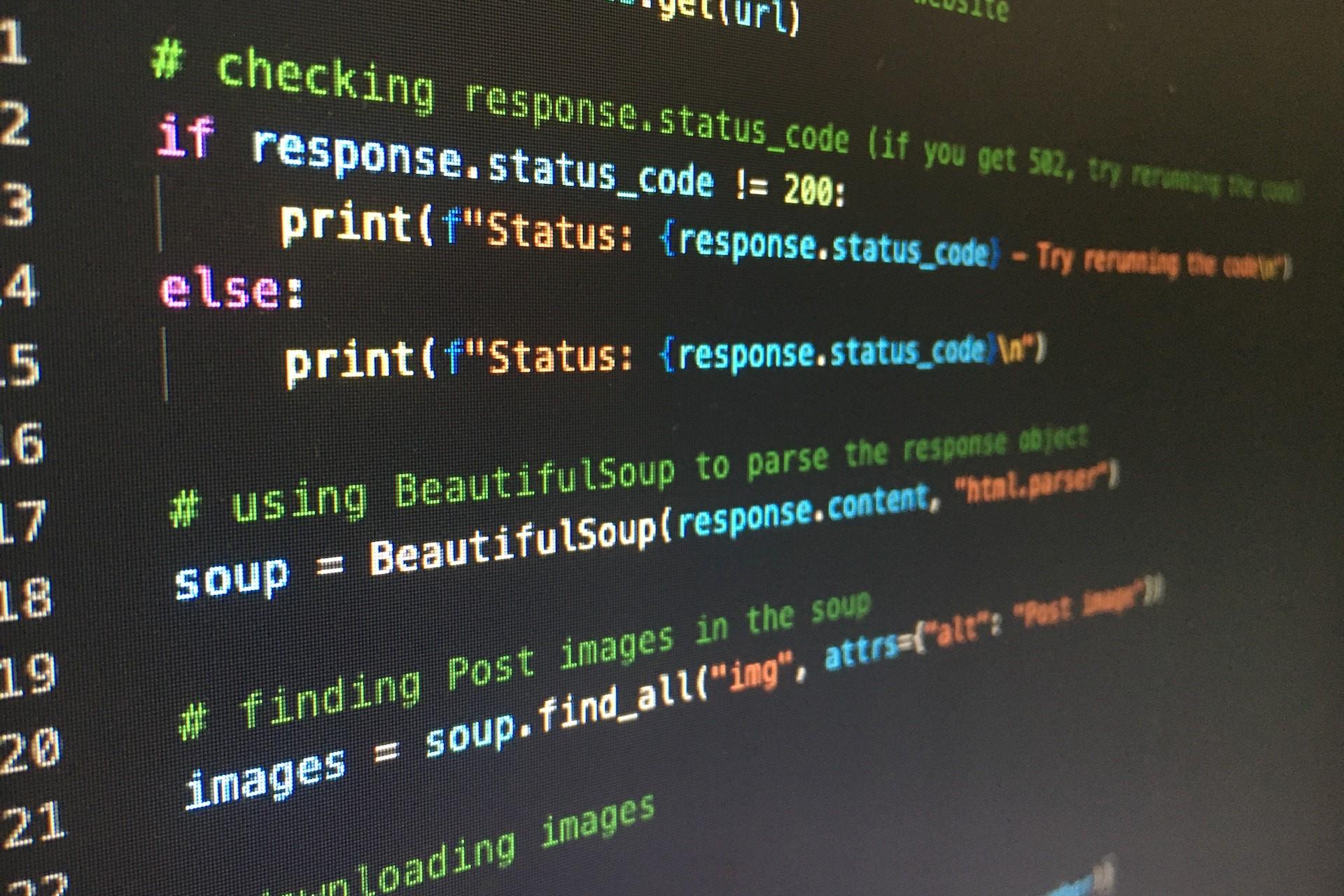
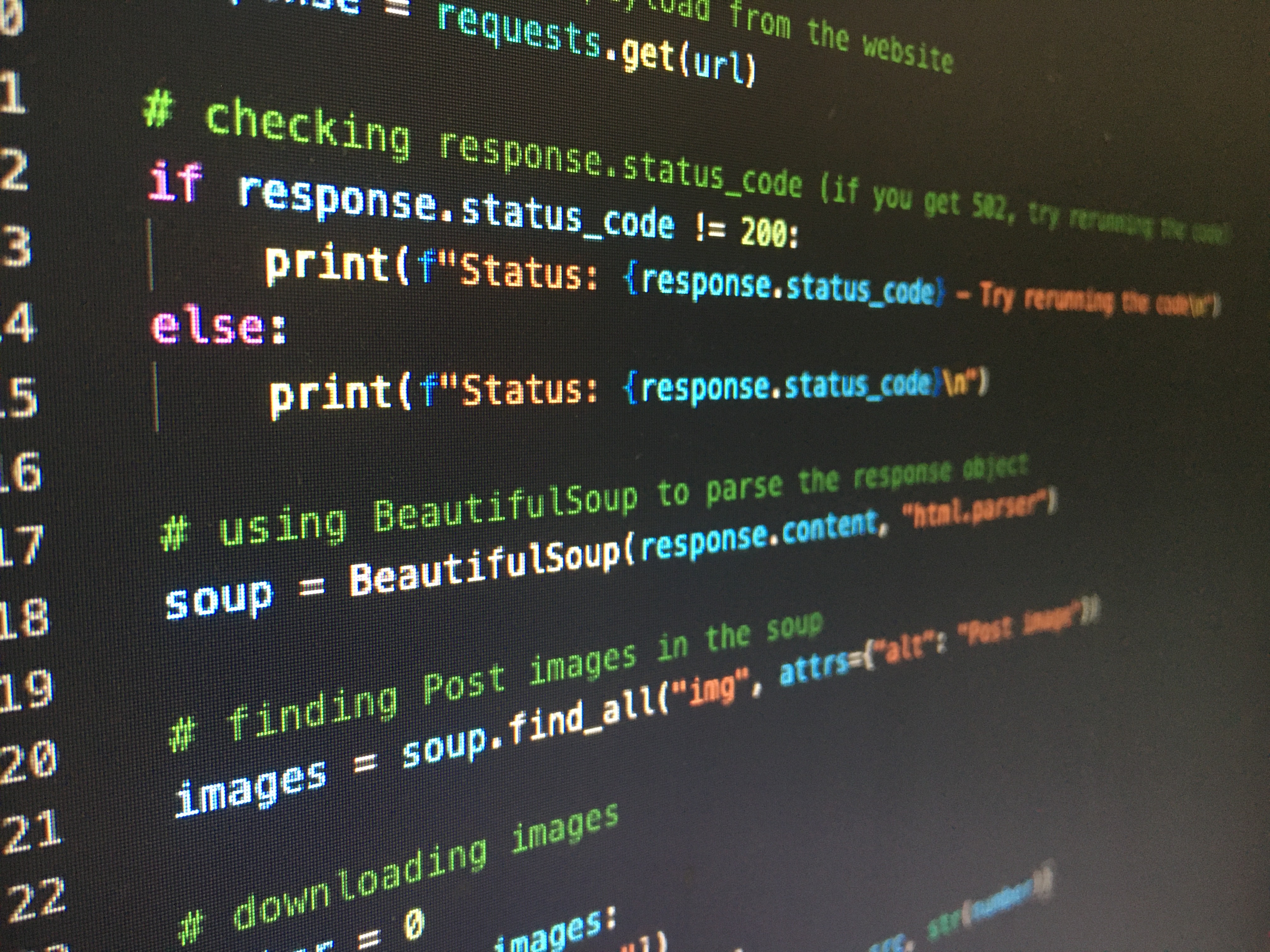
No matter what Python tutorial you decide to use, the first step you will need to take is the installation of Python on your computer. That is necessary for your machine to be able to interpret Python code and run Python functions correctly.
To do that, you simply need to go to the Python official website and download the installer file. It won't be the same depending on your operating system, so you should be careful with that.
Once Python is installed, you can run a Python file on your computer. However, your goal is, of course, to create your own code, so you'll also need to download a programming text editor.
We recommend you to use IDLE for that purpose, which is actually a bit more than a simple text editor because it also includes a debugger and a compiler that can be very useful when working with data.
As soon as you have these two programs on your computer, you can start writing simple code, which should be enough to get an introduction to Python. You can find a tutorial or an online course explaining the basic programming concepts that you can build on later.
Here are some of the crucial notions you should master to work with data.
Data types
The most basic thing we need to learn to start programming is data types. Python doesn't handle text, numbers and truth values in the same way, so you'll deal with data types constantly throughout your learning and work.
So, to make a short introduction, here are the four main data types you need to come to grips with to become good at Python programming:
- string,
- integer,
- float,
- boolean.
A string can be defined as simply a chunk of text. You can have a long string as well as a short string, you can combine strings and even more importantly, you can print them on your screen.
That last point is so relevant because once you've processed your data, you'll want to present it in a user-friendly way and for that, you'll need to print text explaining what has actually been done.
Another important detail is that to declare a string you should put your statement in quotation marks to let Python know your intent.
Next, an integer is a term that you may know from your school math course. It refers to a number with no fractional part like 1, 2, 3, 1005 and so on. What makes an integer different from a string is that you can do math operations with it. For example, you can tell Python to calculate the sum of two integers.
A float is a bit similar to an integer in that it represents a number but a float can also include a fractional part, like 1.02, 3.05, etc. If you need more precision, you should use a float, if you don't an integer is enough.
Finally, a boolean is a truth value that can be either True or False. You can use it in a function when you need to check a statement or if the sum of integers is what you expect it to be.
If you understand these four concepts and why they are important, you are probably good to start programming with Python. If not, we recommend you to look for a course or tutorial on data types because it's really important.
There is more on Python resources in our article.

Other important concepts in the Python language include set, list, dictionary, loop, class and function. You'll explore them step by step as you advance in your learning and become able to use them efficiently to process data.
Start taking python course Melbourne here.

Creating your first Python program
It is a tradition in programming that when we start learning to code in a new language, we should learn the code to print a "Hello world!" statement on our screen.
That is very simple to do in Python especially as you already know what a string is. The only thing you need in addition to that is the print() command that does the rest of the job.
As you've certainly noticed, we have added a pair of brackets after the word print. That is where the statement to print should go. So, your first line of code should look like that in the end:
print("Hello world!")
Try to type that in your text editor, save it as a .py file and then run the program. You should normally see the statement "Hello world!" appear in your Python shell.
Congratulations! You have created your first code in the Python language.
Find out about python course online here.
Using Python libraries
Python is a very versatile programming language because you can import modules of code into your programme and use classes and functions that have been developed by other programmers or by yourself.
A good example of a Python library is Pygame. As its very name indicates, its main function is to help programmers create video games. With Pygame, you can set gameplay parameters, create a list of characters and change the visual style of your game.
Once you've finished developing a particular feature, you can test it and save your code into your file. Once a given file is ready, you don't need to worry about it anymore and can focus on other aspects of your programme.
Another widely used Python library is Pandas. Its main area of application is data science, which naturally makes it interesting for all kinds of businesses, from banks to entertainment websites.
With Pandas, you can read and write data, organise it in the way that suits you, look for patterns and present your results in a clear way.
Some of the areas where Pandas are used are Finance, Economics, Neuroscience, Statistics, Web Analytics, Advertising and many others.
It can be useful to learn Pandas both if you want to start a career as a data analyst and if you already work in one of those areas. With Python and Pandas, you can greatly improve your performance by analysing bigger amounts of data and by making the machine do repetitive tasks.
All you need to get started in Pandas, Pygame or any other library is to learn the basic syntax of the language. The main principles of Python apply to all its modules as well, so you'll be able to make sense of most code you can come across if you know the basics.
If you want to know more about the different uses of Python, have a look at our article.
Python compared with other languages
What makes Python a rather accessible programming language is that most of its commands are perfectly understandable if you speak English.
For example, we have already seen how to use the print function in Python. Some other English words the language uses include class used to create a class, set and list used to convert objects into a set and a list respectively, or if used to set a condition.
Many other programming languages don't function like that at all. For example, in Java, you need to write at least three lines of code to print a "Hello world!" statement, which makes it far less accessible for beginners than in Python.
At the same time, some of the programming tools, such as loops and if-statements, are present in many programming languages in one form or another. This means that after you've mastered Python, learning a new programming language will become much easier.
You can discover the differences between Python and Java in our article.
Summarise with AI: