The terms cosmology, astronomy, and astrophysics are often used together, sometimes even interchangeably. All three fields have to do with the study of the universe, but they each focus on different aspects. Each specialty focuses on a different realm of space; together, they can be used as different lenses to paint a fuller picture of the mysteries of the universe.
| Astrophysics | Cosmology | Astronomy | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Main Focus | Interactions between galaxies, etc | Universe as a whole | Individual celestial objects |
| Primary Goal | Explain physical and chemical processes in space | Understand the universe’s structure and history | Understand celestial bodies and their cycles, movement patterns, and qualities |
| Question Asked | How does it work? | Why is the universe the way it is? When did the universe begin? What will happen in the future? | What is out there? |
| Topics | Gravity, fusion, light, matter | Dark matter, expansion, the Big Bang | Planets, stars, galaxies, meteors |
| Methods | Physics-based modeling, observation | Large-scale data, CMB radiation | Observation |
| Tools | Telescopes, particle detectors, spectometers, satellites, space probes | Mathematical models | Telescopes, spectroscopy, radio telescopes |
| Scale | Stars, planets, galaxies (generally, or specific ones and their relationships with each other) | Entire universe | Local to galactic space |
| Time Focus | Lifetime of a star; Stellar and galactic lifetimes | Billions of years; all time | Present and recent past |

Defining Astronomy
Astronomy is the study of celestial objects and events outside of Earth’s atmosphere.
The Milky Way galaxy and celestial objects like comets, asteroids, stars, and several planets can all be observed with the naked eye. It’s harder now with all the light pollution and satellites orbiting the earth, but before electricity, everyone all over the world spent a lot of time gazing at the night sky and making observations over time.
Observation is still the primary method astronomers use to gather data. Now, however, there are more sophisticated tools at their disposal.
Even before any advanced equipment was invented, ancient astronomers were using observations and calculations to discover realities about the world. In the 3rd century BCE, Aristarchus of Samos was able to determine that the Earth revolves the sun. Around this time, Eratosthenes was also able to calculate the size of the Earth and the axial tilt by measuring shadows. His conclusions were almost exactly what modern-day measurements conclude.
Ancient astronomy was also used to create calendars!
Scope and Focus
Astronomy exists to answer the questions “what exists in space?” and “where are the things in space located?”
Astronomers track observable data like movement patterns, brightness, distance, and composition of objects in space.
Astronomers observe:
- Earth’s moon and the moons of other planets
- Planets and exoplanets
- Comets, asteroids, and meteors
- Stars and their life cycles
- Galaxies and nebulae
Many discoveries in astronomy come from analysing large data sets that have been collected over long periods of time. The data is meticulously measured and recorded so that it can be used years later for further research. It takes a long time for many celestial bodies to move; for example, Pluto completes one revolution around the sun every 248 years, and it was discovered in 1930, so we have only observed about half of Pluto’s year so far.

Methods and Tools
Where ancient astronomy could be done with the naked eye, weak telescopes, and basic tools like sundials, modern astronomy relies on advanced technology. Astronomers focus on collecting data about what celestial bodies exist and where, and how they behave. Movement and physical features are the most relevant pieces of data.
The most common equipment includes:
- Optical telescopes
- Radio telescopes
- Space-based telescopes
These tools help astronomers understand the physical qualities of what they find, like size, shape, and topography.
Notably, astronomers also use spectroscopy, which analyses light from other stars and galaxies. It helps provide information on the subject, such as the chemical composition, temperature, and speed and direction of movement.

Subfields of Astronomy
There are several subdisciplines in astronomy. Some of the most well-known are:
- Observational Astronomy: Gathering and analysing data from observations.
- Theoretical Astronomy: Developing models to explain astronomical phenomena.
- Radio Astronomy: Using radio waves to study celestial objects.
- Ultraviolet Astronomy: Observation of electromagnetic radiation at ultraviolet wavelengths.
- X-Ray Astronomy: Observation of electromagnetic radiation at X-ray wavelengths.
- Gamma-ray Astronomy: Observation of electromagnetic radiation at gamma-ray wavelengths.
- Galactic Astronomy: Study of the Milky Way galaxy.
- Extragalactic Astronomy: Study of everything outside of the Milky Way galaxy.
- Gravitational-Wave Astronomy: Detection and study of gravitational waves.
- Neutrino Astronomy: Gathers information about astronomical objects by collecting and observing the neutrinos they emit.
Find out which subfield of astronomy suits you best with a physics tutor Melbourne.
Astrology is not a science, but it has to do with observations about the movement patterns of celestial bodies. In ancient times, it went hand-in-hand with astronomy, since both were seen as scientifically viable subjects. However, astrology was found to be unscientific and separated from other studies in the 18th century. Astrology is a belief system that is sometimes tied to religion and spirituality; it has to do with zodiac signs, astrological charts, and divination.
Defining Cosmology
Cosmology is the study of the universe at the largest possible scale. Rather than looking at individual stars or planets, cosmologists study the overall structure of the entire cosmos and use the data to piece together the history of the universe.
Early thoughts about cosmology include ancient Hindu beliefs from about 2,000 BCE, which suggested that the universe was infinitely large and existed in 8-billion-year cycles. Ptolemy of ancient Greece suggested that the universe was arranged with Earth at the centre.
Scope and Focus
Modern cosmology seeks to find the answers to the biggest questions we have:
- What is the origin of the universe?
- How big is the universe?
- How has the universe changed over time?
- How might the universe change in the future?
- Will the universe last forever, or will it eventually end?
Cosmologists think on a grand scale, in terms of light-years and eons. They piece together the story of the creation of the universe by observing how groups of planets and galaxies behave currently and extrapolate how they came to be in their current state. They study theories like the Big Bang, trying to piece together the mystery of how the universe formed and why stars, planets, and galaxies exist as they do.
Find out what cosmologists and astrophysicists think about extraterrestrial life.
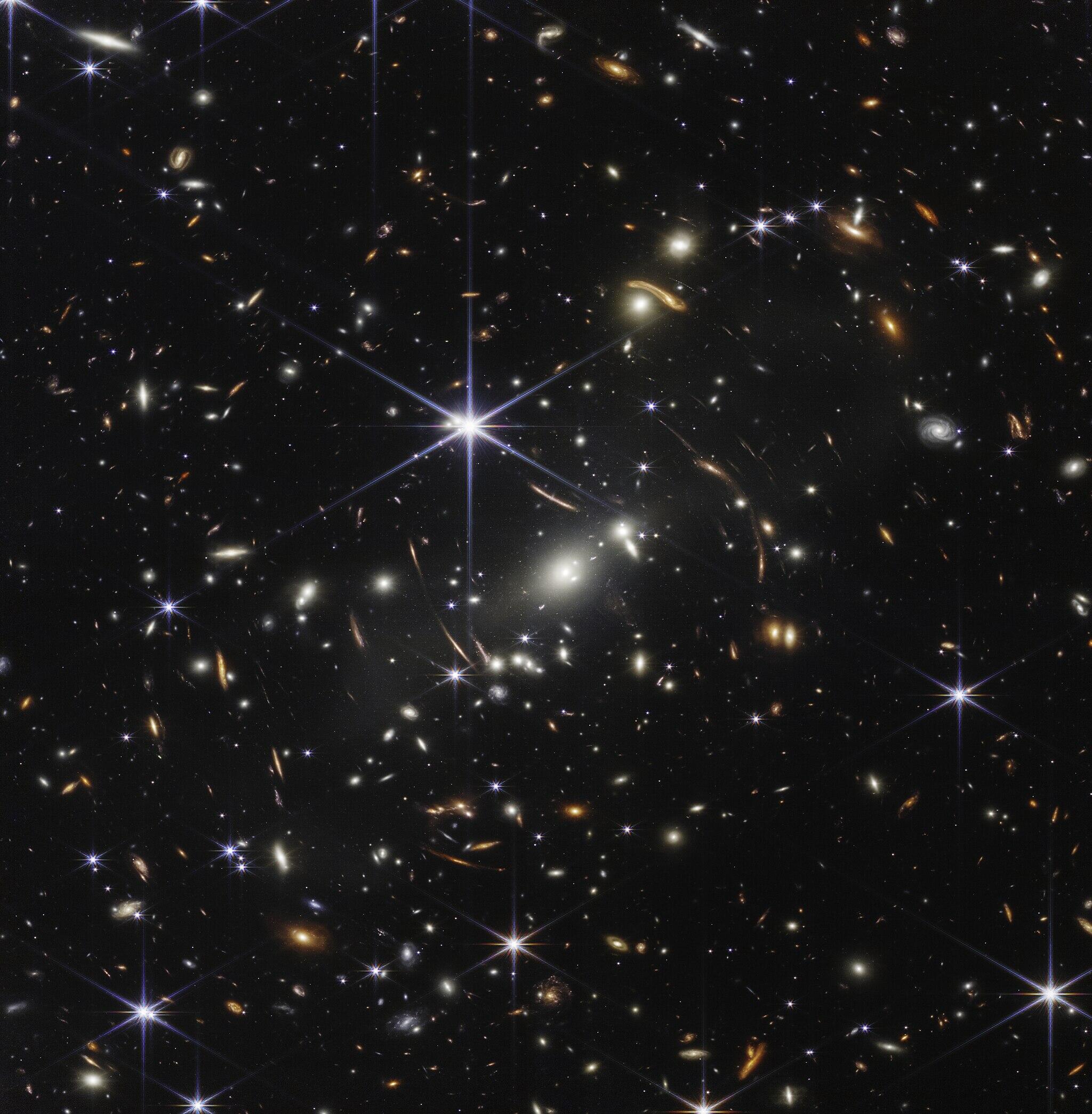

Methods and Tools
Cosmologists use a lot of the same data as astronomers, but they interpret and use the data differently. Instead of focusing on the movement or physical qualities of individual celestial objects, they look for patterns among the web of all things in space to determine context on a larger scale.
In addition to the same methods astronomers use, cosmologists also:
- Analyse cosmic microwave background (CMB) radiation
- Conduct large-scale surveys of galaxies to understand the overall structure and distribution
- Build mathematical models and simulations based on general relativity
They use many computer simulation programs to test hypotheses, understand change over time according to existing data, and theorise about what could happen in the future. The simulations can demonstrate how different models of the universe might behave over time with different factors.
Key Concepts in Cosmology
Cosmologists are the scientists who have posited some of the most influential and game-changing theories about the universe. Since cosmologists are mostly researching the origins of the universe, they have come up with grand theories that can be difficult to comprehend unless you’re well-versed in the science of space and time
The Big Bang Theory
Probably the most well-known cosmological concept, the Big Bang Theory suggests that everything in the universe once began as a tiny, hot, dense point that rapidly expanded. It says that everything in the universe is still expanding outward from one central point where it all began. It’s supported by multiple types of evidence, including CMB radiation and observable galaxy expansion. It combines observational astronomy and particle physics.
Learn about the Big Bang and more with a private physics tutor on Superprof!
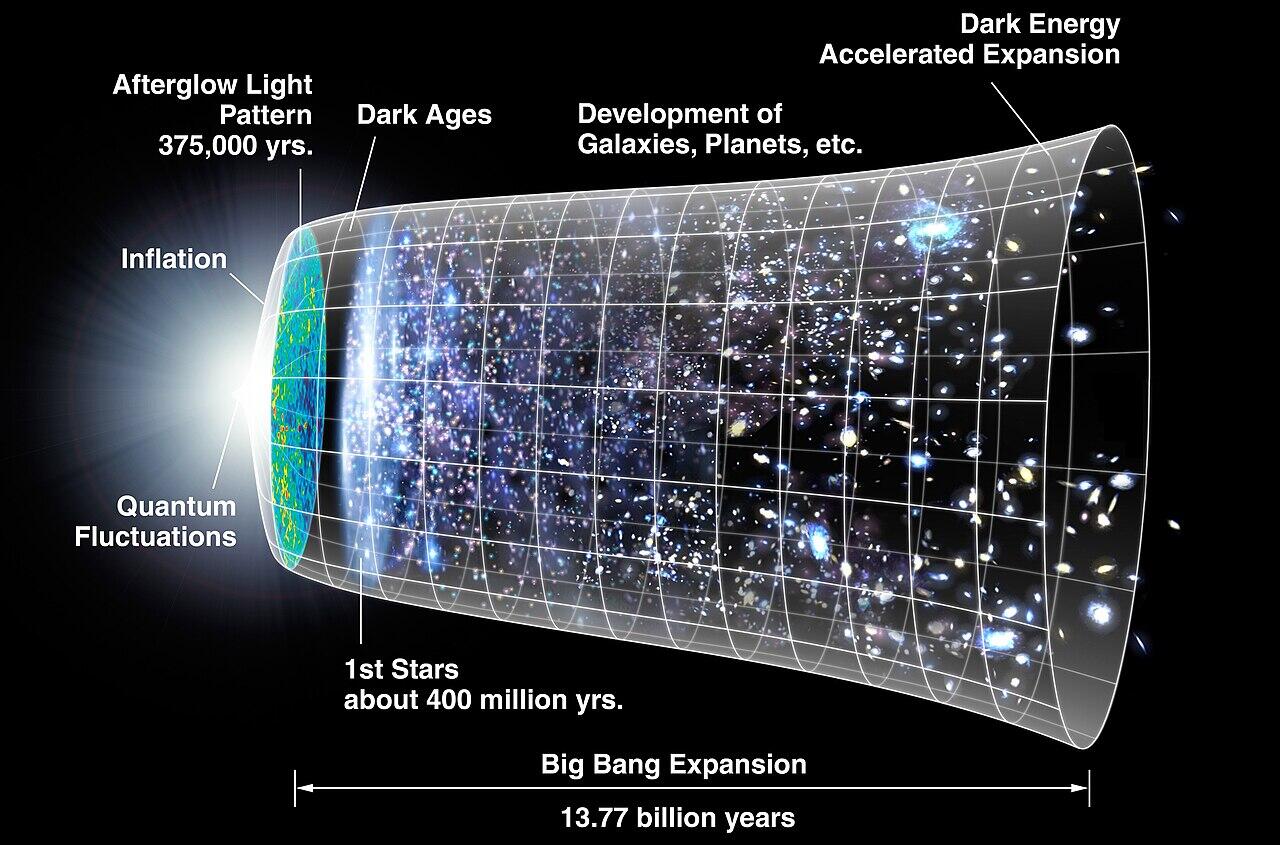
Dark Matter and Dark Energy
These theoretical concepts are used as a way to explain how and why galaxies form and move. They are not directly observable, but their existence can be implied from other data. They are critical in the Lambda-CDM model of cosmology. Together, they make up most of the universe’s total mass and energy.
Expansion of the Universe
Dark energy is a key component in the accelerated expansion of the universe. Observations show that the universe is constantly expanding, with galaxies moving away from one another. This discovery has changed the way scientists understand time, distance, and cosmic history.
While physical cosmology focuses solely on the scientific data associated with mapping the universe and determining its factual history, philosophical, religious, and mythical cosmology disciplines focus on the non-scientific parts. There is great value in contemplating the meaning of it all on a spiritual level, especially in an anthropological sense.

Comparing Astronomy and Cosmology
Cosmology and astronomy are closely connected, and cosmology can be considered a subfield of astronomy. They are like two sides of a scientific coin. Both often rely on the same type of data, but the way they use it is different. Each can utilise data from the other discipline to further the research in their own.
Overlapping Areas
Both fields concern the study of the observable characteristics of celestial bodies. Astronomers and cosmologists both seek out the same information, often using the same tools.
Tools used by both:
- Telescopes
- Satellites
- Specific detectors
- Mathematical models
- Physics
Data used by both:
- Observational celestial phenomena
- Light (spectroscopy)
- Thermodynamics
- Electromagnetism
- Mechanical, etc.
Both disciplines collect similar data; the difference lies in how they analyse and apply it. In essence, both disciplines use astronomical data, but cosmologists take the data analysis a step further.
Cosmologists must have a firm grasp on astronomy and how to collect, refine, and utilise the data in order to do their job.
They often share data with one another, since each science is able to discern different conclusions. This shared data can help each science progress as they focus on their individual specialties and techniques.
Want to learn more about space? Find effective Physics courses on Superprof.

Distinct Differences
The biggest difference between the two disciplines is scale: astronomy focuses on individual objects in local systems, while cosmology focuses on the entire universe.
For example, astronomers might focus on a planet and its movement within a solar system. Cosmologists would focus on that solar system and its relation with nearby systems and the other things (dust, gas, and stars) that form a galaxy, as well as the relationships between galaxies, where they are located in space, and how that information can be used to determine the history and future of the universe.
Both sciences are necessary and work in tandem to uncover the intricate workings of the world around us.

Introducing Astrophysics
In modern science, astrophysics more or less encompasses all of astronomy; the difference being that it uses a lot of theories and principles of physics rather than just observational data.
It is the connection between astronomy and cosmology, using advanced scientific techniques and theories to study specific objects, not the whole universe.
Definition and Scope
Astrophysics is the study of the physical and chemical properties of celestial objects. Beyond the astronomy information about size, movement, shape, and other basic physical features like radio signals, astrophysics delves into the physical and chemical natures of things.
Using the laws of physics like gravity, thermodynamics, nuclear physics, electromagnetism, and quantum mechanics, astrophysics seeks to find information like:
- How do stars produce energy through fusion?
- What happens to matter in a black hole?
- How do planets, stars, and galaxies form?
- How does gravity affect planets and other objects in space?

Relationship with Astronomy and Cosmology
Astrophysics, in a way, provides the “rules” for cosmology and astronomy. It serves as a bridge between pure observation (astronomy) and theory (cosmology). Since each discipline would be severely limited if it only ever adhered strictly to its own realm, they must work together like departments in a company.
- Astronomy finds and provides data. Example: There is a star that is changing colour
- Astrophysics explains what is being seen. Example: The star is cooling down because it’s losing fuel, which causes a colour change
- Cosmology uses this data, combined with many other datapoints, to discern information about that solar system or galaxy. Example: The cooling star indicates something about the age of that solar system and the type of matter found there, which can be used to glean more information about that sector of the galaxy
It’s not a straightforward line between each discipline. Indeed, they overlap in a variety of ways that might differ by research institute or subject, project, team, or individual scientist.
Differences Between Astrophysics and Cosmology
Astrophysics and cosmology are very similar in many ways. They both use high-level math, physics, and chemistry to evaluate objects and phenomena in space. However, their “lenses” are different.
Focus Areas
Like astronomy, astrophysics focuses on the smaller scale. It looks at the chemical composition, physical behaviour of light, and other qualities of an individual planet or star. They may compare objects that are nearby one another to understand their comparative chemical makeups, etc., but they don’t expand the view to the macro scale. They focus on specific systems.
Cosmologists look at the same type of information, but on a much larger scale. Instead of considering the temperature of one star, they look at the overall temperature of an area light-years wide. They want to see the entire universe’s “landscape” instead of the individual features within. This helps them understand the history of the universe, which can only be understood by looking at the largest-possible picture. They focus on global (or rather, universal) patterns.
One of the great challenges of modern cosmology is to discover what the geometry of the universe really is.
Margaret Geller
Methodologies
Cosmology is much more theoretical, while astrophysics is much more observational. So, the scientists work in different ways.
Astrophysicists often conduct laboratory experiments and gather data with scientific tools. For example, they may use particle accelerators to simulate the high-energy environments found in the centres of stars. They also use probes, satellites, telescopes, and other observational tools to gather data about the visual appearance, gravitational qualities, radiowaves and radiation, etc., of a celestial body. They’ll also use theoretical physics to conclude why and how the object of their study exists and behaves the way it does.
Cosmologists generally use the data from experiments and observations made by astrophysicists and astronomers to make theories and discoveries on a larger scale. They’ll use large datasets to map out information and find patterns that can only be seen when examining at a zoomed-out level. They use mathematical models and statistical analysis of cosmic data to make theories and conclusions.
No single field has all the answers to the questions of the universe. They work together to create a fuller picture of the universe. When learning about astronomy vs astrophysics vs cosmology, the key to understanding is remembering the goal of each science. Astronomy seeks to see what exists, astrophysics seeks to explain how they function, and cosmology seeks to use these clues to figure out the past and future of the universe.
Summarise with AI:















